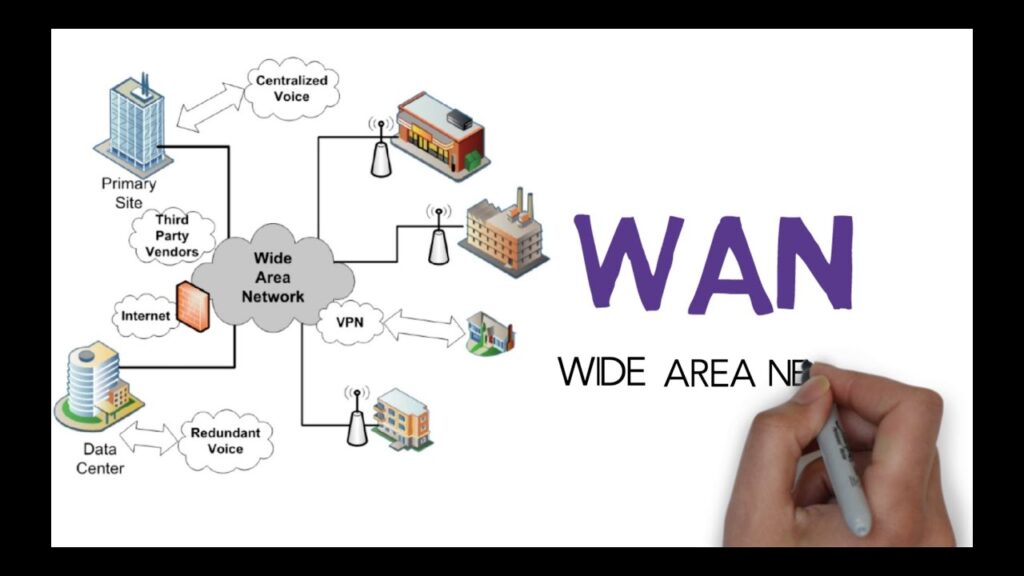
WAN technology combines services for accumulating, storing, and processing data and tools for working with data in a globally connected network. There are technologies of communication platforms, for example, PubNub, which allow real-time processing of data from such global networks, assigning them the property of computer networks.
Computers (combined into one of five classes of networks), applications, and cloud storage should be considered as components of wide-area networks. The elements of such networks can be located anywhere in the world. For example, Dworkz, a UX design firm in San Francisco, shares its experience on what a WAN is and how it works in business.
For reference
According to the scale criteria, there are five classes of networks:
- Global networks, in fact – WAN.
- City networks — MAN.
- Corporate networks — EAN.
- Local — LAN.
- Personal — PAN.
The network for collecting, processing, and interpreting information is formulated depending on the goals and scale of the company. The more complex the business structure, the more types of networks are used.
Introductory information
In a total sense, the global computing network is a combination of computers located at a remote distance for the everyday use of the world’s information resources. The most extensive vast area network is the Internet. This is a network of numerous international networks connected by servers that store big data. The servers are operated with the help of communication and computing applications. There are more than 200 such networks. To access this data, analyze it according to specified criteria and use it – there are applications for this. The latter allows you to create closed wide area networks for business.
Why do you need a WAN for business?
Modern enterprises use wide area networks for several reasons, including the globalization of business processes, the digitalization of products, the interactive communication with customers, and the large databases businesses operate. For example, a customer service-oriented business uses a WAN to:
- Communicate with clients using voice and video apps;
- All employees of the company have access to the database to create new data, delete old ones and analyze the processes of the first and second;
- Use unified local customer service tools,
- Connect to cloud services;
- Run and host internal applications.
Consequently, wide area networks help modern businesses quickly learn about new market trends and implement new solutions even faster. The WAN also helps create trends. With WAN technology, all this can be done securely, efficiently, and highly personalized.
WAN – how it works
The architecture of WANs is based on Open Systems Interconnection (OSI). The purpose of these systems is to standardize and visualize the interaction process between WAN end users. There are seven levels of WAN control points, each using different network technologies. The following is a list of seven levels, organized on a user-to-global basis:
- User level.
Here, with the help of applications, users enter and display information from the global network.
2. Applied level.
At this level, data is encrypted and transmitted to the network.
3. Session level.
This layer opens and closes every single communication session between different devices on the same network.
4. Transport level.
At this level, the system works within the framework of TCP protocols that assemble connection data into request and response packets.
5. Network level.
The data transmission route over the global network is determined at this level.
- The link level forwards data packets from one device to another and controls the start and end of this process.
- At the “physical” level, data is directly transmitted as digital bits using various network media – via optical cables and wireless technologies.
At each level, the system operates within the specified protocols. These relate to security, unification, and data routing. On the client side, applications help interpret the data.
LAN vs. WAN
You can also consider local networks, such as LANs, as an integral part of the WAN. Such networks have limited performance but high data transfer rates. Private networks typically use a single communication technology. There is no conflict between the global and local networks: the first type has many network technologies, the task of which is to provide communication and data processing between various networks of the second type. In addition, local area networks are used in business focused on both customers and business partners.
WAN and business idea
Suppose you have a travel company with branches in 39 countries worldwide. Different languages, different currencies, forms of payment, and different target audiences, as well as competitors, all require close attention to avoid going out of business. A wide area network helps to monitor business processes, and a local network unites the central office with peripheral offices into a single system.
For your business, you need an application whose task is to collect information confidentially, analyze it, and interpret it based on the experience of both your company and competitors’ benchmarks. Our partners develop such applications from Dworkz. Furthermore, they provide technical support for the operation of applications, updating these and introducing new features.
Output
A successful business becomes successful if it can be automated and scaled up. Two additional conditions for staying in business are 1) digitalization and 2) the search for the best solutions. To collect relevant information about competitors, you need to collect it from the World Wide Web. You require a closed local network to implement the best experience in your own business.
The intersection point of your central office and peripheral branches, as well as the global and local networks, is an application that forms a structured wide area network from its constituent parts. It’s a tool that helps you analyze your business for strengths and weaknesses, so you can quickly apply the best world experience in this industry. This is how the booking.com hotel booking system works. Focus on the best so that, in time, you become an example.