Diabetes is a chronic disease caused when your blood sugar or blood glucose level turns too high. Blood glucose is considered as one of the main sources of energy, found in the food we eat. It reaches our body cells through insulin, a pancreatic hormone that helps transferring glucose from foods to our body cells. There are conditions when our body reduces or stops making insulin at all and as a result, the glucose stays in the blood without reaching the body cells.
If not checked on time, this glucose in our blood increases and causes health issues, one of which is diabetes. Diabetes is not curable, but by taking several preventive measures, we can keep it controlled, reducing further health complications.
In this blog, we have come up with the information on types of diabetes, its symptoms and complications. Overall, everything you must know about this chronic disease to lead a healthy life.
What are the types of diabetes?
There are different types of diabetes, but the most common ones include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
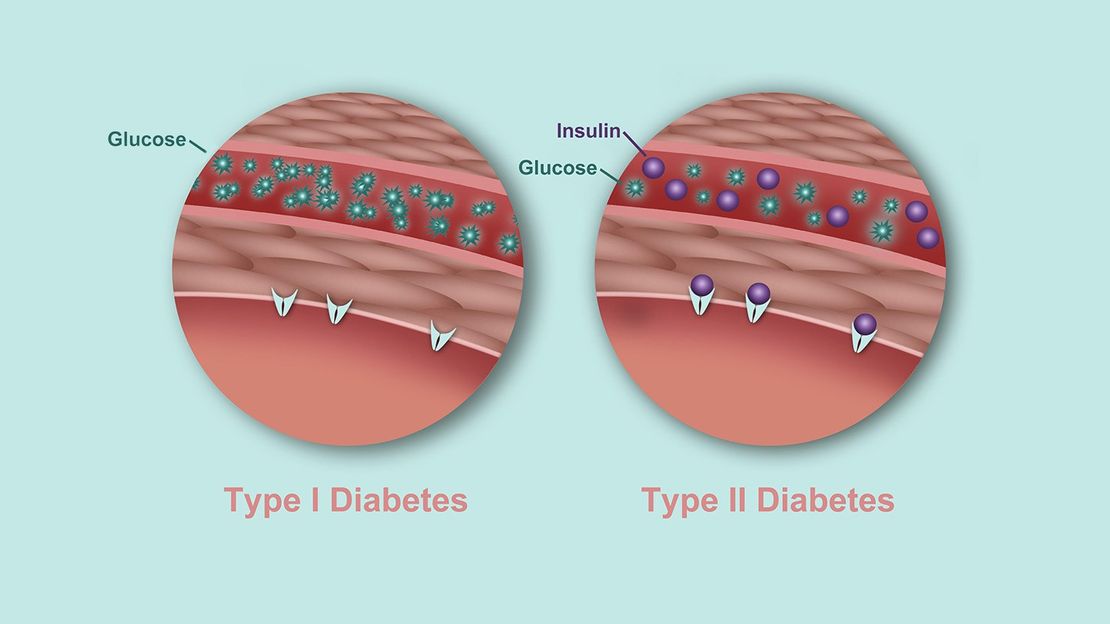
1. Type 1 diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, our body stops making insulin as the immune system starts attacking the pancreas, destroying the cells making insulin in the process. This type of diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults. However, it can occur at any age. The condition gets so severe that people require daily insulin dosages to stay alive.
2. Type 2 diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, our body stops making or using insulin properly. This type of diabetes can develop at any age. The most common group of people affected by type 2 diabetes are middle-aged and older adults. It is the most common type of diabetes diagnosed so far.
3. Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed in pregnant women. In most cases, it goes away after the baby’s birth. However, if a woman is affected by gestational diabetes, she is more likely to be attached by type 2 diabetes, later in her age.
Other types
Other uncommon types of diabetes include cystic-fibrosis-related diabetes and monogenic diabetes. Monogenic diabetes is the inherited form of diabetes, which runs in a family from generations.
Let us discuss about type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes in detail, as these are the most common types of the chronic disease.
Type 1 Diabetes
Of all the diabetic people, around 10% have type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is the result of an autoimmune reaction in which our body’s defense system starts attacking the cells that secrete insulin. The body this, stops producing insulin. The exact cause of this reaction is still unknown, but it is something related to both environmental and genetic conditions.
Type 1 diabetes can be diagnosed at any age, but commonly seen affecting children and young adults. People affected by type 1 diabetes require taking insulin injection daily to stay alive. It is to keep the blood sugar levels in control.
Researchers are still conducting studies to find the exact risk factors of this type of diabetes. If you have a family member with type 1 diabetes, you are likely at a higher risk of getting it too. Environmental factors and viral infections are linked to the factors causing type 1 diabetes.
In the present time, it is impossible to prevent type 1 diabetes. Why? The environmental triggers that are suspected to be initiating the process of elimination of the insulin-producing cells in the body are still being investigated.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms
The main symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
- Sudden weight loss
- Bedwetting
- Frequent urination
- Abnormal thirst and dry mouth
- Constant hunger
- Lack of energy, tiredness
- Blurred vision
Based on these symptoms of type 1 diabetes alone, diagnosing the disease is not possible. So, some additional tests are carried out for accurate report
Handling type 1 disease
People with type 1 diabetes must have access to insulin injections every day. Along with this, it is important to monitor the blood glucose level, maintain a healthy lifestyle and exercise regularly to manage type 1 diabetes conditions.
Insulin
There are different types of insulin prescribed on the basis of the conditions of the patient. Each type works differently. Some work quickly, while others peak and some others last longer. Generally, a physician gives insulin through a syringe, an insulin pump or using an insulin pen.
Types of insulin:
1. Rapid-acting: This type of insulin is normally taken with or before a meal. It acts in very short time to limit the increase in the blood sugar levels, which happened post eating. It is very important to avoid overdose to reduce any chance of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). This type of insulin includes Lispro, Asparat, Glulisine.
2. Short-acting: this type of insulin is usually taken before eating. Also called as neutral or regular insulin, it doesn’t act very fast like rapid-acting, so, considered appropriate for some people. Short-acting insulin includes Humulin R, Actrapid, Insuman Rapid.
3. Long-acting: These are type of insulin that can last in the body for almost a day. Doctors recommend taking it early morning or at night before sleeping. Some common long-acting insulin are Glargine and Detemir.
4. Intermediate-acting: A physician recommends intermediate-acting insulin along with short-acting insulin. It starts to act with an hour and follows a period of peak which lasts for around 7 years. Some of the most popular intermediate-acting insulin include Protaphane, Humulin NPH and Insulatard.
Insulin Treatment Plans
If the condition worsens, most doctors recommend the following two insulin treatment plans:
Basal bolus regimen: In this treatment plan, the doctor suggests the short-acting insulin with meals, mostly three times a day. Along with short-acting insulin, your doctor will also recommend intermediate-acting insulin once or twice in a day.
Twice-daily insulin: This treatment plan include using both intermediate-acting insulin and short-acting insulin, twice a day.
Self-monitoring
SMBG or Self-monitoring of blood glucose is a process where a diabetic patient with type 1 diabetes checks the blood glucose levels every day at work, home, school or anywhere else. The process of self-monitoring helps taking the right amount of insulin daily and their doctors get to know the changes in their regular blood glucose levels throughout the day. This way, the treatment plan can be adjusted well.
Medical experts recommend diabetics with type 1 diabetes to check their blood glucose for a minimum of four times in a day.
Healthy nutrition
Healthy nutrition is an important management technique of type 1 diabetes. You must ensure having a healthy diet, excluding food that affects the blood glucose levels negatively. Include healthy foods like eating unsaturated fats like nuts, olive, avocado, vegetable oils, etc in place of saturated fats such as cheese, butter, cream, etc. Start eating dietary fiber and quit tobacco consumption, added sugar and alcohol.
Exercise
Exercising is another important activity to adapt to control type 1 diabetes. Go for a morning walk every day. If that’s not your cup of tea, try doing aerobics, cycling or go swimming. Whatever you do, make sure you stay active and healthy.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is another common type of diabetes, in fact, the most common as per the survey. It accounts for almost 90% of the total diabetic cases.
Characterized as insulin resistance, the body stops responding to insulin in type 2 diabetes. As insulin doesn’t function properly, the blood glucose level keeps on increasing, releasing more and more insulin. In some cases of type 2 diabetes, the patient’s pancreas might just exhaust over time, producing less or no insulin at all, causing even more increased blood sugar levels. The condition is called hyperglycemia.
Type 2 diabetes is more common in older adults, sometimes in middle-aged people. However, young adults, children and teenagers also come under the risk of this chronic disease because of physical inactivity, poor diet and increasing risk of obesity.
Type 2 diabetes symptoms
Most symptoms of type 2 diabetes are same as type 1 diabetes, like:
- Frequent urination
- Slow healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
- Lack of energy, tiredness
- Recurrent infections in the skin
- Excessive thirst and dry mouth
- Blurred vision
These symptoms are initially mild or might be even absent in some people having type 2 diabetes. People having type 2 diabetes have longer life than people with type 1 diabetes. But, it is still important to go for regular health checkups, so that you can start the medications on time.
Risk Factors of type 2 diabetes
There are numerous risk factors that can lead to type 2 diabetes, such as:
- Family history of diabetes
- Unhealthy diet
- Increasing age
- Overweight
- Poor nutrition during pregnancy
- Physical inactivity
- Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)*
- High blood pressure
- Ethnicity
- History of gestational diabetes
Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) is a condition when the blood glucose level is more than normal but less than the line of diagnosing diabetes.
Physical activity and change in diet due to urbanization and rapid development have increased the total number of people suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Handling of type 2 diabetes
The best way of handling the problem of type 2 diabetes by living a healthy lifestyle which involves regular exercise/physical activity, a healthy diet, balanced weight (some weight loss tips) and no smoking.
After a certain period of time, diabetics with type 2 diabetes need to take oral medications as maintaining a healthy lifestyle doesn’t seem enough for controlled blood sugar levels. Doctors also prescribe combination of therapy and medications.
For worsened conditions of type 2 diabetes, insulin injections are the last option for the patient.
Medications for type 2 diabetes
Generally, oral medications for people having type 2 diabetes include:
- Metformin: It lowers insulin resistance, allowing your body to use insulin effectively. It is the first kind of treatment for type 2 diabetes. So, your doctor is more likely to prescribe you tablets containing metformin as the main component.
- Sulfonylureas: It stimulates your pancreas to boost the production of insulin. Sulfonylureas include glipizide, glibenclamide, tolbutamide, glimepiride and gliclazide.
What are the possible complications in diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease that brings along several complications in form of further health issues. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels lead to increasing risks of health problems that can even lead to death. Some of the most serious complications include:
- vessel disease, leading to heart attack or stroke
- amputations due to neuropathy or vessel disease
- eye problems, called retinopathy
- nerve damage, or neuropathy
- infection or skin conditions
- kidney damage, or nephropathy
Type 2 diabetes can also increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. So, make sure you have your blood sugar levels under control all the time.
Complications during pregnancy
Poor nutrition during pregnancy can lead to gestational diabetes in women. If you already have diabetes, your high blood sugar levels can be harmful both you and your baby, as it increases risks of:
- Stillbirth or miscarriage
- Birth defects
- High blood pressure
- Preeclampsia
How common is diabetes in the United States?
According to trusted sources, almost 30.3 million people have diabetes in the United States. Out of these, 90-95% have type 2 diabetes while 5-10% have type 1 diabetes.
In the year 2015, doctors diagnosed around 1.5million adults with diabetes. Add the numbers! Not just this, suspicions says more 84.1million to have prediabetes, but most often don’t know about the condition or that they have it.
Prediabetes is a stage when the blood glucose level rises than the normal limit, but is not as high to be diagnosed as diabetes.
If you have a family history of diabetes, you are at a higher risk of getting the disease.
How will I know I have diabetes?
To know if you have diabetes, you will have to undergo blood tests to check your blood glucose levels. In case you notice any earlier symptoms of diabetes, you should see a doctor. However, there are even cases when people are unaware that they have diabetes because of no sign of symptoms.
In a Nutshell
Diabetes, a chronic disease that has no particular age of occurrence can be a serious health issue for patients who are already having other chronic health problems like high blood pressure, cholesterol problems, etc.
There are two main types of diabetes – Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes. Each of these types has there own set of symptoms. You should see a doctor as soon as you come across any of the above-mentioned symptoms.